Databricks Delta Lake Data Modeling
Deliver a reliable single source-of-truth for all data
Delta Lake is an open-source storage layer that brings reliability to data lakes. It was initially developed by Databricks in 2016 and open-sourced to the Linux Foundation in 2019. Delta Lake provides ACID transactions, scalable metadata handling, and unifies streaming and batch data processing. It is a storage layer on top of cloud object stores (Amazon S3, Azure Data Lake Storage, Google Cloud Storage and others) or distributed filesystems like HDFS, which describes and defines the formats of data object and transaction logs, and a set of access protocols enabling DBMS-like features. It is fully compatible with Apache Spark APIs. Its schema enforcement automatically handles schema variations to prevent insertion of bad records during ingestion. The Databricks Lakehouse platform provides data engineering, SQL analytics, data science and Machine Learning on Azure Databricks, Databricks on AWS and Google Cloud.
Hackolade Studio was specially adapted to support the data modeling of Delta Lake, including the Databricks storage structure of clusters, databases, tables and views. It leverages Hive primitive and complex data types, plus user-defined types. And combines it all with the usual capabilities of forward-engineering of HiveQL scripts, reverse-engineering, documentation generation, model comparison, command-line interface integration with CI/CD pipelines, etc...The Hackolade Studio application closely follows the Delta Lake terminology.
Try Hackolade Studio for FREE
There's no risk, no obligation, and no credit card required!
Just access the application in your browser.
No credit card. No registration. No download. Runs in browser. No cookies. Local storage of models. Security first.
Databricks Data Modeling Tool
The data model in the picture below is a sample data model that is featured in this tutorial.
It provides a simple overview of the data structures featured in this Databricks Delta Lake environment in the Hackolade Studio, so that users can do all kinds of useful actions with the data model.
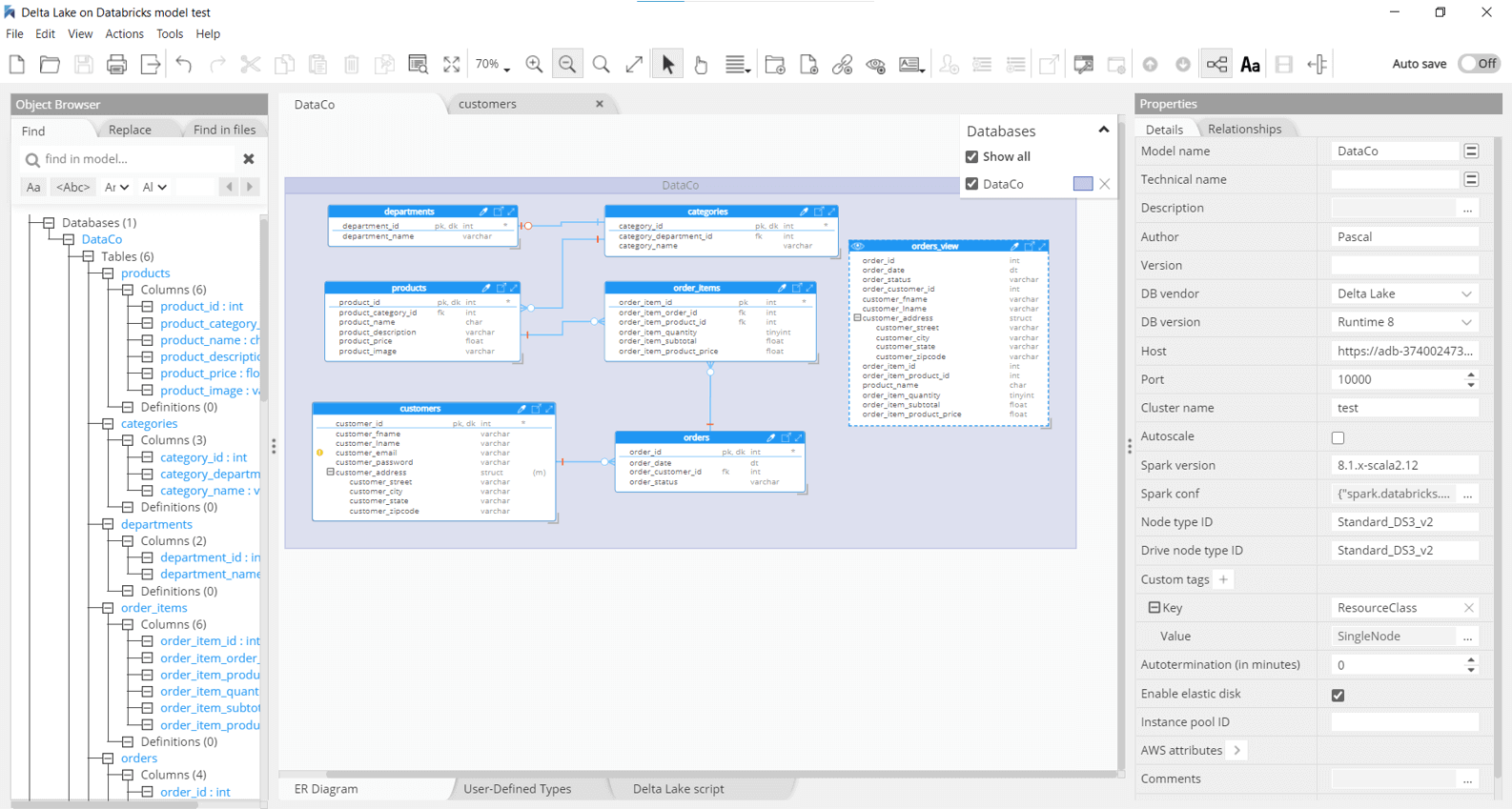
Schema visualization
Hackolade helps users to better understand and work with their Databricks Delta Lake data by providing them with a visual representation of the structure of the data that is stored inside their Databricks Delta Lake environment.
Components of a Databricks Delta Lake Data Model
A data model for the Databricks Delta Lake consists of several different components.
First, there are clusters: a set of computation resources and configurations on which you run data engineering, data science, and data analytics workloads. On these clusters, you have databases: a collection of tables that belong together. These tables then represent a collection of structured data that can be queried with Spark APIs and Spark SQL. The table is logically made up of the data being stored in cloud object stores (Amazon S3, Azure Data Lake Storage, Google Cloud Storage and etc) or distributed filesystems like HDFS. The table metadata describes the layout of the data in the table and defines the formats of data object and transaction logs, and a set of access protocols enabling DBMS-like features. Its schema enforcement automatically handles schema variations to prevent insertion of bad records during ingestion.
A Databricks view is a searchable object in a database, which can be defined by a query. Data cannot be stored in a view, as it is a sort of virtual table. By using joins, it is possible to combine data from one or more tables. It may also hold a subset of information.
Every Databricks deployment has a central Hive metastore accessible by all clusters to persist table metadata. Instead of using the Databricks Hive metastore, users have the option to use an existing external Hive metastore instance or the AWS Glue Catalog.
Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD)
The ER diagram displays the tables, data elements of the tables, as well as the relationships between the data elements.
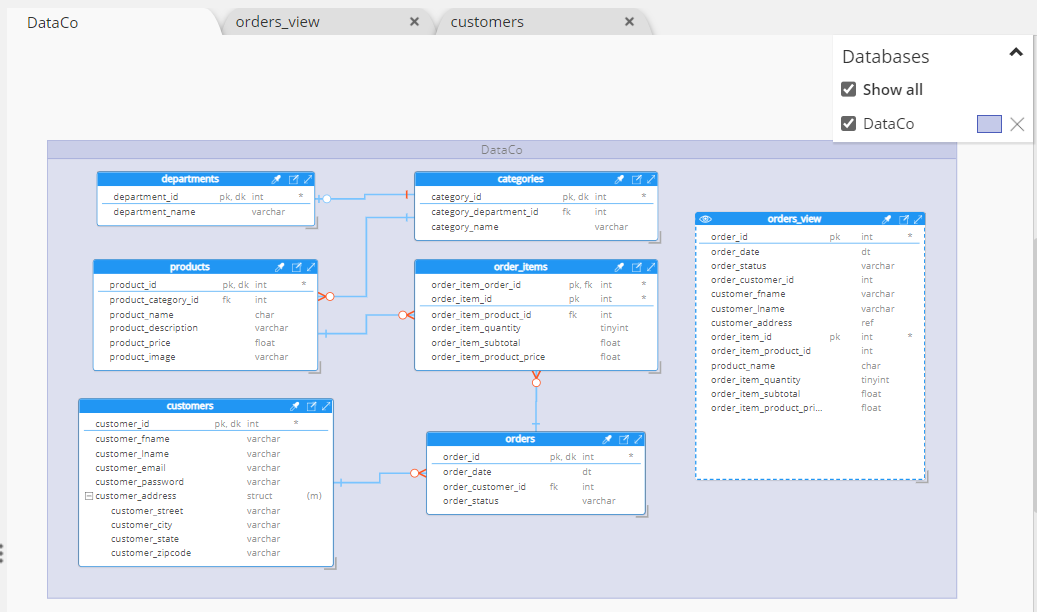
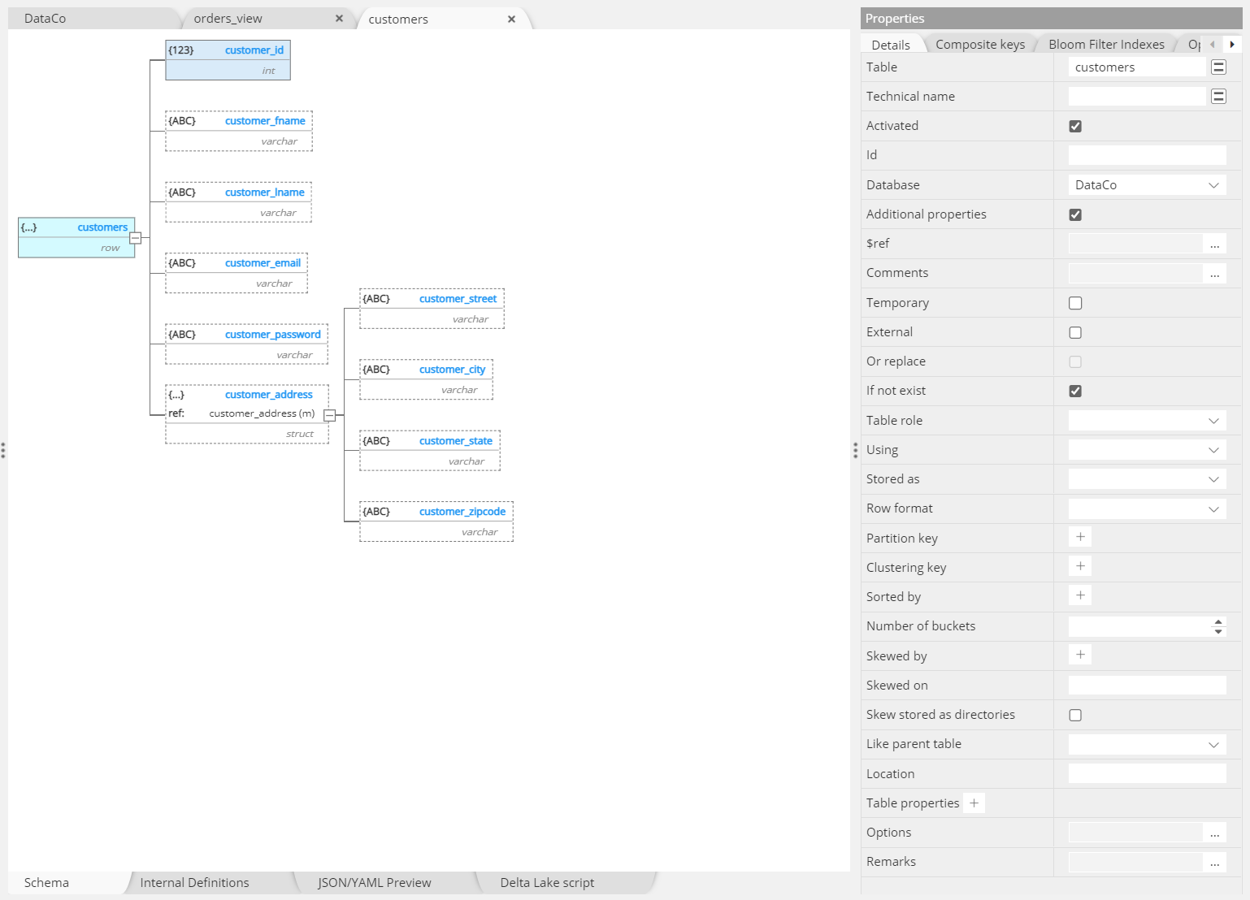
Hierarchical view of nested objects
A Databricks Delta Lake data model is described with definitions of properties and constraints for each table and field. Hackolade Studio represents these fields in a convenient and easy to read hierarchy, with a “Properties” pane to the right that immediately allows the user to understand the details of a particular data element. This can be supplemented with detailed descriptions and a log of team comments gathered as the model adapts over time for the schema evolution.
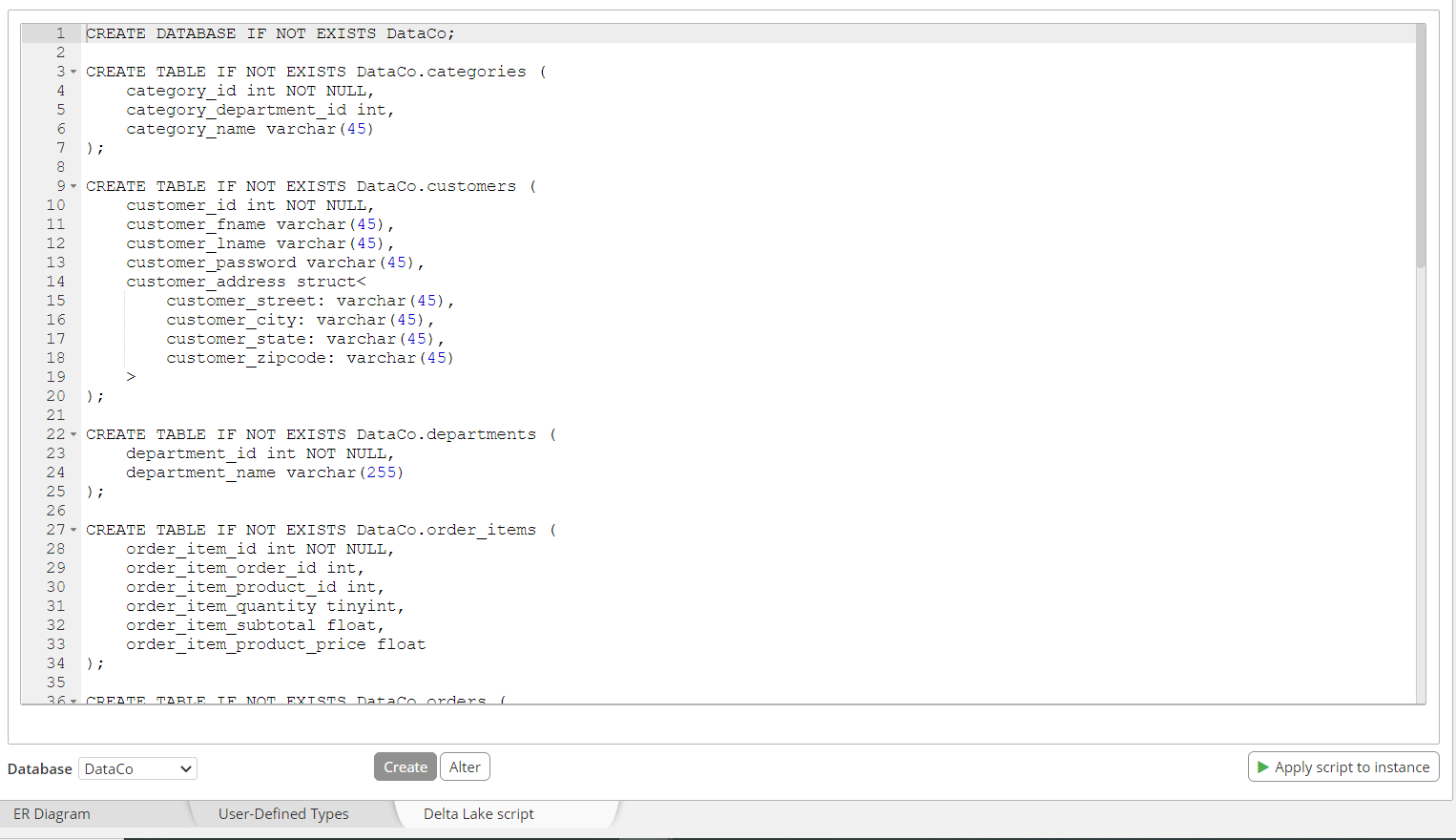
Outputs of a Schema Design tool for Databricks
In addition to the DDL script that is generated for the specific Databricks Delta Lake data model that you are working on, Hackolade Studio also provides the possibility to generate the HTML, PDF, or Markdown documentation that includes all the diagrams, tables, relationships, and metadata of the Databricks Delta Lake data model.
Databricks Unity Catalog
The Unity Catalog is a unified governance solution for data and AI assets on the Databricks Lakehouse. It provides centralized access control, auditing, lineage, and data discovery capabilities across Databricks workspaces. It was introduced with Runtime 11.3
All data in Unity Catalog is referenced using a three-level namespace: catalog.schema.table.
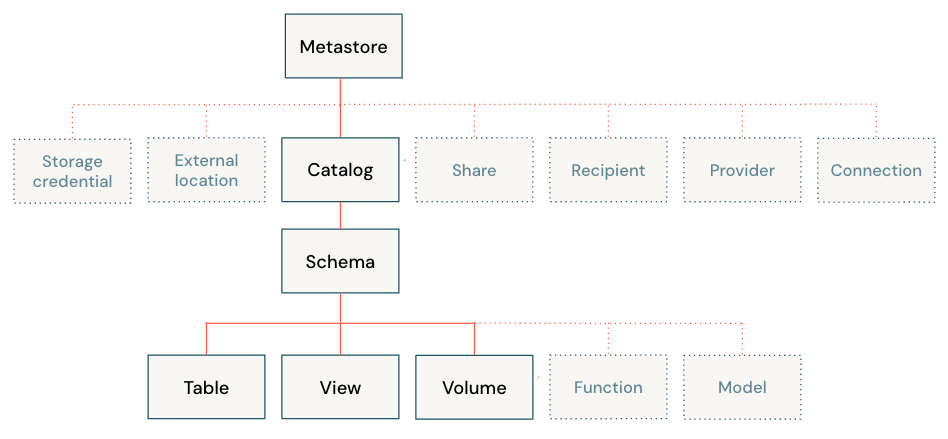
Catalog
Catalogs are the highest level in the data hierarchy (catalog > schema > table/view/volume) managed by the Unity Catalog metastore. They are intended as the primary unit of data isolation in a typical Databricks data governance model. Catalogs represent a logical grouping of schemas, usually bounded by data access requirements. Catalogs often mirror organizational units or software development lifecycle scopes. You may choose, for example, to have a catalog for production data and a catalog for development data, or a catalog for non-customer data and one for sensitive customer data.
Schema (Database)
Schemas, also known as databases, are logical groupings of tabular data (tables and views), non-tabular data (volumes), functions, and machine learning models. They give you a way to organize and control access to data that is more granular than catalogs. Typically they represent a single use case, project, or team sandbox.
Tables
Tables reside in the third layer of Unity Catalog’s three-level namespace. They contains rows of data. Unity Catalog lets you create managed tables and external tables.
Views
A view is a read-only object derived from one or more tables and views in a metastore.
Volumes
Volumes reside in the third layer of Unity Catalog’s three-level namespace. They manage non-tabular data. You can use volumes to store, organize, and access files in any format, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. Files in volumes cannot be registered as tables.
For more information on the Unity Catalog, consult the documentation.
Benefits of Data Modeling
A data model provides a blueprint for applications that closely represent the understanding of complex data-centric enterprises. Hackolade increases data agility by making data structures transparent and facilitating its evolution. The benefits of data modeling for Databricks are widespread and measurable.
Schema design is a best practice to ensure that applications evolve, scale, and perform well. A good data model helps reduce development time, increase application quality, and lower execution risks across the enterprise.
Free trial
To experience the first Databricks data modeling tool and try the full experience of Hackolade Studio free for 14 days, download the latest version of Hackolade Studio and install it on your desktop. There's no risk, no obligation, and no credit card required! The software runs on Windows, Mac, and Linux, plus it supports several other leading NoSQL databases. Or you can run the Community edition in the browser.
Try Hackolade Studio for FREE
There's no risk, no obligation, and no credit card required!
Just access the application in your browser.
No credit card. No registration. No download. Runs in browser. No cookies. Local storage of models. Security first.